Last update:
Plants & Animals news

Researchers: Heat is coming for our crops—we have to make them ready
Australia's vital agriculture sector will be hit hard by steadily rising global temperatures. Our climate is already prone to droughts and floods. Climate change is expected to supercharge this, causing sudden flash droughts, ...
Plants & Animals
19 minutes ago
0
0

Saturated soils could impact survival of young trees planted to address climate change
The saturated soil conditions predicted to result from increased rainfall in the UK's upland regions could have a knock-on effect on the ambition to create more woodland in the fight against climate change, a new study has ...
Plants & Animals
1 hour ago
0
5

Global warming may boost mosquito habitats, study finds
A research team at Los Alamos National Laboratory is using computer models to simulate how climate change could expand the geographical range in which mosquitoes live, which may cause an increase in mosquito-borne illness. ...
Plants & Animals
19 hours ago
0
9

Scientists find ancient, endangered lamprey fish in Queensland, 1400 km north of its previous known range
The Australian brook lamprey (Mordacia praecox) is part of a group of primitive jawless fish. It's up to 15 cm long, with rows of sharp teeth. Surprisingly, it doesn't use these teeth to suck blood like most lamprey species—it's ...
Plants & Animals
19 hours ago
0
2

Saving the Mary River turtle: How the people of Tiaro rallied behind an iconic species
Australian freshwater turtles are facing an alarming trend. Almost half of these species are listed as vulnerable, endangered or critically endangered.
Plants & Animals
23 hours ago
0
6

'Essentially a gas station,' fishy feast draws sea lions to Pier 39 in numbers not seen in 15 years
They're big, loud, and smelly—and they have taken over San Francisco's touristy Pier 39.
Plants & Animals
May 8, 2024
0
10

Woodlice hold the new record for smallest dispersers of ingested seeds
Even bugs as small as woodlice can disperse seeds they eat, setting a new record for smallest animal recorded to do so. The Kobe University discovery underscores the crucial yet often overlooked role that small invertebrates ...
Plants & Animals
May 8, 2024
0
5

Discovery of ancient Glaswegian shrimp fossil reveals new species
A short but robust little shrimp may have died out over 330 million years ago during the Carboniferous period, but the rare Scottish shellfish has been revitalized as a new species to science and as a Glaswegian.
Plants & Animals
May 8, 2024
0
52

Model predicts future spread of box tree moth in North America
CABI scientists have led research with collaborations from the University of Toronto and University of Guelph, both in Canada, to update a model which predicts the future spread of the box tree moth (Cydalima perspectalis) ...
Plants & Animals
May 8, 2024
1
0

Regulating branch development of petunias
Branching is a pivotal determinant of plant architecture, not only influencing the capacity of the plant to adapt to its environment but also significantly impacting crop yield, ornamental characteristics, and production ...
Plants & Animals
May 7, 2024
0
6

Snap bean panel reveals variability in leaf, pod color phenotypes
A new study led by researchers from Oregon State University explores the significance of vegetable color in consumer choices and agricultural production, focusing on snap beans. The color of snap bean pods, influenced by ...
Plants & Animals
May 7, 2024
0
34

Bsal and beyond: Task force helps stave off amphibian disease threat
Amphibians—like frogs and salamanders—are the most imperiled group of animal species in the world; infectious diseases are among the greatest threats to their existence. After a decade of research, a scientific task force ...
Plants & Animals
May 7, 2024
0
12
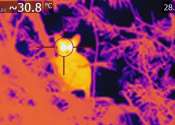
In South Africa, tiny primates could struggle to adapt to climate change
In the "sky islands" of the Soutpansberg Mountains of South Africa, two closely related species of primate jostle for space. One is the thick-tailed greater galago (Otolemur crassicaudatus), also known as a bushbaby, which ...
Plants & Animals
May 7, 2024
0
106

Aquatic weed among 'world's worst' expands in northeastern US
An article published in the journal Invasive Plant Science and Management provides new insights on a northern hydrilla (Hydrilla verticillata) subspecies (lithuanica) and its establishment outside the Connecticut River.
Plants & Animals
May 7, 2024
0
5

Deep sea mining could be disastrous for marine animals
In a recent study published in Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, researchers of Wageningen University & Research and the University of Bergen have shown that release of deep-sea mining particles can ...
Plants & Animals
May 7, 2024
0
15

Study demonstrate improved root growth in radio-cesium contaminated soil
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science (CSRS) have identified a way for plants to gain resistance to cesium, a radioactive toxin that can be found in contaminated soil. After manipulating a specific ...
Plants & Animals
May 7, 2024
0
7

Chimps shown to learn and improve tool-using skills even as adults
Chimpanzees continue to learn and hone their skills well into adulthood, a capacity that might be essential for the evolution of complex and varied tool use, according to a study published May 7 in the open-access journal ...
Plants & Animals
May 7, 2024
0
223

Discovery of structural specialization in myriapod ovaries
Elaborate observations reveal the structural specialization within an epithelial layer covering oocytes in the Japanese pill-millipede, Hyleoglomeris japonica, considered absent in Myriapoda. Comparing this result with previous ...
Plants & Animals
May 7, 2024
0
20

Grizzlies are returning to Washington's North Cascades. How will that work?
Among the jagged peaks of the North Cascades, lush alpine meadows rich with berries and wildflowers blanket valleys carved by glaciers, some threaded with trickling creeks.
Plants & Animals
May 7, 2024
0
2

New Vincetoxicum species found in Yunnan
Vincetoxicum is a genus of plants in the Apocynaceae family. It is distributed in Asia, especially in mountainous areas, and most of the known species occur in China and Japan. The extended Vincetoxicum includes about 150 ...
Plants & Animals
May 7, 2024
0
0
More news
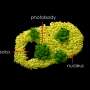
Free-forming organelles help plants adapt to climate change

Why parrots sometimes adopt—or kill—each other's babies

Listening to giants: The search for the elusive Antarctic blue whale

Bee body mass, pathogens and local climate influence heat tolerance

Lego-pushing bumblebees reveal insect collaboration dynamics

NASA is helping protect tigers, jaguars, and elephants—here's how
Other news

Changes in pig farming in the 20th century spread antibiotic-resistant Salmonella around the world, finds study
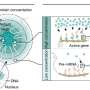
Genes spatially organize for efficient mRNA splicing, study shows
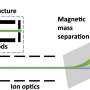
Probing neptunium's atomic structure with laser spectroscopy

How aging clocks tick: New study points to stochastic changes in cells
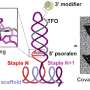
New DNA origami technique promises advances in medicine

London's runaway horses remind us that animals are workers too
Marine sharks and rays 'use' urea to delay reproduction, finds study

New study reveals phonon properties of β-MoB₂ single crystal

Getting dirty to clean up the chemical industry's environmental impact

Team develops an epigenome editing toolkit to dissect the mechanisms of gene regulation