Study could mean greater anticipated global warming

Global climate models disagree widely in the magnitude of the warming we can expect with increasing carbon dioxide. This is mainly because the models represent clouds differently. A new modeling approach successfully simulates the observed cloud fields in a key region for climate. The study finds a greater tendency for clouds to thin with global warming than in any of the current climate models. This means the expected warming may be greater than currently anticipated.
Current state-of-the-art global climate models predict substantial warming in response to increases in greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide. The models, though, disagree widely in the magnitude of the warming we can expect. The disagreement among models is mainly due to the different representation of clouds. Some models predict that global mean cloud cover will increase in a warmer climate and the increased reflection of solar radiation will limit the predicted global warming. Other models predict reduced cloudiness and magnified warming. In a paper that has just appeared in the Journal of Climate, researchers from the University of Hawaii Manoa (UHM) have assessed the performance of current global models in simulating clouds and have presented a new approach to determining the expected cloud feedbacks in a warmer climate.
Lead author Axel Lauer at the International Pacific Research Center (IPRC) at UHM notes, "All the global climate models we analyzed have serious deficiencies in simulating the properties of clouds in present-day climate. It is unfortunate that the global models' greatest weakness may be in the one aspect that is most critical for predicting the magnitude of global warming."
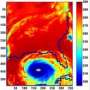
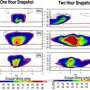
To study the clouds, the researchers applied a model representing only a limited region of the atmosphere over the eastern Pacific Ocean and adjacent land areas. The clouds in this region are known to greatly influence present climate, yet current global models do poorly in representing them. The regional model, developed at the IPRC, successfully simulates key features of the region's present-day cloud fields, including the observed response of clouds to El Nino. Having evaluated the model's simulation of present-day conditions, the researchers examined the response of simulated clouds in a warmer climate such as it might be in 100 years from now. The tendency for clouds to thin and cloud cover to reduce was more pronounced in this model than in any of the current global models.
Co-author Kevin Hamilton concludes, "If our model results prove to be representative of the real global climate, then climate is actually more sensitive to perturbations by greenhouse gases than current global models predict, and even the highest warming predictions would underestimate the real change we could see."
More information: Lauer, A., K. Hamilton, Y. Wang, V. T. Phillips, and R. Bennartz (2010), The Impact of Global Warming on Marine Boundary Layer Clouds over the Eastern Pacific - A Regional Model Study, Journal of Climate, Vol. 23, No. 21, 5844
Provided by University of Hawaii at Manoa