Spanish scientists search for fuel of the future

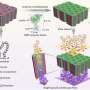
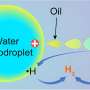
In a forest of tubes eight metres high in eastern Spain scientists hope they have found the fuel of tomorrow: bio-oil produced with algae mixed with carbon dioxide from a factory.
Almost 400 of the green tubes, filled with millions of microscopic algae, cover a plain near the city of Alicante, next to a cement works from which the CO2 is captured and transported via a pipeline to the "blue petroleum" factory.
The project, which is still experimental, has been developed over the past five years by Spanish and French researchers at the small Bio Fuel Systems (BFS) company.
At a time when companies are redoubling their efforts to find alternative energy sources, the idea is to reproduce and speed up a process which has taken millions of years and which has led to the production of fossil fuels.
"We are trying to simulate the conditions which existed millions of years ago, when the phytoplankton was transformed into oil," said engineer Eloy Chapuli. "In this way, we obtain oil that is the same as oil today."
The microalgae reproduces at high speed in the tubes by photosynthesis and from the CO2 released from the cement factory.
Every day some of this highly concentrated liquid is extracted and filtered to produce a biomass that is turned into bio-oil.
The other great advantage of the system is that it is a depollutant -- it absorbs the CO2 which would otherwise be released into the atmosphere.
"It's ecological oil," said the founder and chairman of BFS, French engineer Bernard Stroiazzo-Mougin, who worked in oil fields in the Middle East before coming to Spain.
"We need another five to 10 years before industrial production can start," said Stroiazzo-Mougin, who hopes to be able to develop another such project on the Portuguese island of Madeira.

"In a unit that covers 50 square kilometres, which is not something enormous, in barren regions of southern Spain, we could produce about 1.25 million barrels per day," or almost as much as the daily export of oil from Iraq, he said.
BFS, a private company, hopes to negotiate "with several countries to obtain subsidies for the installation of artificial oil fields," he said.
Other similar projects being studied in other parts of the world.
In Germany, the Swedish energy group Vattenfall last year launched a pilot project in which algae is used to absorb carbon dioxide from a coal-fired power plant.
US oil giant ExxonMobil plans to invest up to $600 million in research on oil produced from algae.
Companies, in particular those in the aeronautic sector, have shown keen interest in this research, hoping to find a replacement for classic oil.
(c) 2011 AFP