Gold nanoparticles bring scientists closer to a treatment for cancer
Scientists at the University of Southampton have developed smart nanomaterials, which can disrupt the blood supply to cancerous tumours.
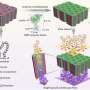
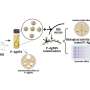
The team of researchers, led by Physics lecturer Dr Antonios Kanaras, showed that a small dose of gold nanoparticles can activate or inhibit genes that are involved in angiogenesis - a complex process responsible for the supply of oxygen and nutrients to most types of cancer.
"The peptide-functionalised gold nanoparticles that we synthesised are very effective in the deliberate activation or inhibition of angiogenic genes," said Dr Kanaras.
The team went a step further to control the degree of damage to the endothelial cells using laser illumination. Endothelial cells construct the interior of blood vessels and play a pivotal role in angiogenesis.
The researchers also found that the gold particles could be used as effective tools in cellular nanosurgery.
Dr Kanaras adds: "We have found that gold nanoparticles can have a dual role in cellular manipulation. Applying laser irradiation, we can use the nanoparticles either to destroy endothelial cells, as a measure to cut the blood supply to tumours, or to deliberately open up the cellular membrane in order to deliver a drug efficiently."
The researchers have published two related papers with another one submitted for publication and four more planned throughout this year. Their major target is to develop a complete nanotechnology toolkit to manipulate angiogenesis.
More information: NanoLett. 2011, 11 (3), 1358 and Small 2011, 7, No. 3, 388.
Provided by University of Southampton