New protein structure expands nature's repertoire of biomolecules

(PhysOrg.com) -- Proteins – the building blocks of life – come in so many different shapes and sizes that it’s easy to think nature must have already exhausted all possible combinations. But, despite millions of years of evolution, it seems there are some forms that nature couldn’t quite reach.
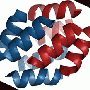
The artificial protein made by the Bristol team – which they have named CC-Hex – has 6 polypeptide chains that the team designed from first principles; that is, whilst the chains take inspiration from biology they are not based on or related to any one particular natural protein. Each chain folds into a helix, and these assemble to form a bundle (see top image).
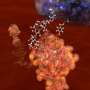
This is interesting because nature appears not to have used this structure, or at least natural analogues of CC-Hex have not yet been observed. Moreover, the structure is intriguing as the helices come together to form a ring that defines a central channel (see middle and bottom images).
-
.jpg)
The protein has a central channel with defined chemistry that can be altered and controlled -
.jpg)
This central channel provides the basis for engineering new proteins such as ion channels, which may be used as components of sensor and purification devices, and catalysts, which could pave the way to new industrial enzymes
The team, led by Professor Dek Woolfson and Professor Leo Brady, has also shown that the chemistry inside the channel can be altered using further design, chemical synthesis and X-ray crystallography.
Despite quite radical changes to the internal chemistry, the protein structure is robust to these alterations. This is exciting because it is precisely how many natural proteins function: they alter chemistry within defined and highly controlled cavities within protein structures. With this in mind, the team believes that CC-Hex represents an exciting opportunity to design new proteins, including enzymes and ion channels, from scratch.
Professor Dek Woolfson said of the discovery: “This is an exciting time for our labs. Not only have we found a part of protein space that nature seems to have neglected, but we believe that the new structure will allow us to engineer protein functions much more rationally and confidently than has been possible before.”
More information: ‘A de novo peptide hexamer with a mutable channel’ by NR Zaccai, B Chi, AR Thomson, AL Boyle, GJ Bartlett, M Bruning, N Linden, RB Sessions, PJ Booth, RL Brady, and DN Woolfson in Nat. Chem. Biol. DOI: 10.1038/NChemBio.692
Provided by University of Bristol