Artificial molecules: Researchers explore novel methods for assembly of quantum dots

(PhysOrg.com) -- Matthew Doty, assistant professor in the University of Delaware Department of Materials Science and Engineering, is co-author of two papers exploring novel methods for assembling quantum dots to control how electrons interact with light and magnetic fields for applications in next generation computing devices and solar energy capture.
The papers recently appeared in Physical Review B, a journal of the American Physical Society (APS). Both papers were selected as “Editor’s Suggestions,” a designation reserved for only five percent of articles submitted to the journal.
Doty’s group studies quantum dots, tiny semiconductors that can trap single electrons in a manner comparable to atoms like hydrogen and helium. Quantum dots are often referred to as “artificial atoms” because they have electronic properties similar to natural atoms. Doty’s group explores the way these “artificial atoms” can be assembled to create “artificial molecules.” Unlike natural molecules, the properties of these quantum dot molecules can be tailored to create unique and tunable properties for the electrons trapped in the molecules.
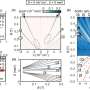
The first paper, entitled “In situ tunable g factor for a single electron confined inside an InAs quantum dot molecule,” documents a new strategy for engineering the spin properties of single confined electrons.
Doty’s team demonstrates this strategy by designing, fabricating and characterizing a quantum dot molecule that allows the electron properties to be tuned with a small change in the voltage applied to the molecule. The success of the strategy validates a new approach to engineering optoelectronic devices with dramatically improved computational power.
The lead author of the paper was Weiwen Liu, a doctoral student in Doty’s research group. Co-authors include UD engineering doctoral students Ramsey Hazbun and Shilpa Sanwlani; James Kolodzey, Charles Black Evans Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering; and Allan Bracker and Daniel Gammon from the Naval Research Laboratory.
The second paper, entitled “Spectroscopic signatures of many-body interactions and delocalized states in self-assembled lateral quantum dot molecules,” describes a different molecular design, in which the two quantum dots are placed side by side instead of one on top of the other. The lateral geometry changes the way in which electrons are trapped in the molecule and creates more complex electronic molecular states. These new electronic states of the lateral molecular design provide a template for new computing architectures that overcome scaling limits of conventional charge-based computing by mediating interactions between single confined spins.
Xinran Zhou, a doctoral student in Doty’s research group, served as the lead author of the paper. Co-authors include UD doctoral students Shilpa Sanwlani and Weiwen Liu and researchers from Kwangoon University of South Korea, the University of Arkansas and the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China.
Journal information: Physical Review B
Provided by University of Delaware