Rearranging the cell's skeleton: Small molecules at the cell's membrane enable cell movement
Cell biologists at Johns Hopkins have identified key steps in how certain molecules alter a cell's skeletal shape and drive the cell's movement.
Results of their research, published in the December 13 issue of Science Signaling, have implications for figuring out what triggers the metastatic spread of cancer cells and wound-healing.
"Essentially we are figuring out how cells crawl," says Takanari Inoue, Ph.D., an assistant professor of cell biology and member of the Center for Cell Dynamics in the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine's Institute for Basic Biomedical Sciences. "With work like ours, scientists can reveal what happens when cells move when they aren't supposed to."
Their new discovery highlights the role of the cell's skeleton, or cytoskeleton, in situations where "shape shifting" can rapidly change a cell's motion and function in response to differing environmental conditions.
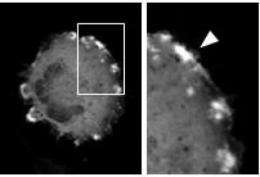
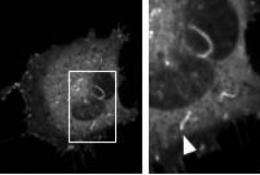
When cell's such as fibroblasts, which gather to heal wounds, move from one place to another, its cytoskeleton forms ripple-like waves or ruffles across its surface that move towards the front of the cell and down, helping pull the cell across a surface. Researchers have shown that these ruffles form when a small molecule, PIP2, appears on the inside surface of the membrane at the front edge of a cell. Until now, however, they have been unable to recreate cell ruffles simply by directing PIP2 to the cell's front edge. Manipulations have instead led the cytoskeleton to form completely different structures, squiggles that zip across the inside of the cell like shooting stars across the sky, which the researchers call comets.
In their experiments, Inoue and his group looked for factors that determined whether a cell forms ruffles or comets. The researchers tried to create ruffles on the cell by sending in an enzyme to the cell membrane that converts another small molecule into PIP2. Using cytoskeleton building blocks marked to glow, the team used a microscope to watch the cytoskeleton assembling itself and saw that this approach caused the cytoskeleton to form comets, not the ruffles that the researchers had predicted.
The team suspected that comets formed because of a fall in levels of another small molecule used to make PIP2, PI4P.
To test this idea, the researchers tried to make ruffles on cells only by increasing PIP2 at the membrane, rather than changing the quantities of any other molecules. Using molecular tricks that hid existing PIP2 then revealed it, the researchers effectively increased the amount of available PIP2 at the membrane. This time the researchers saw ruffles.
"Now that we've figured out this part of how cells make ruffles, we hope to continue teasing apart the mechanism of cell movement to someday understand metastasis," says Inoue. "It will be interesting to manipulate other molecules at the cell surface to see what other types of cytoskeletal conformations we can control," he says.
Tasuku Ueno and Christopher Pohlmeyer of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and Björn Falkenburger of the University of Washington were additional authors of the study.
Provided by Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions