Fujitsu Develops Technology for High-Reliability Gallium Nitride HEMT
Fujitsu Laboratories today announced the development of a new high-reliability technology for high power gallium nitride (GaN) high electron-mobility transistors (HEMT), paving the way for commercialization of high power GaN HEMTs.
The new technology enables the transistors to operate even at the high temperature of 200 degrees Celsius for more than one million hours, equivalent to over 100 years, under pinch-off condition with a drain voltage of 50 volts (50V), thereby enabling the world's longest lifecycle for GaN HEMTs.
Fujitsu will strive toward applying GaN HEMTs using this new technology for the high-speed wireless communications market, such as for satellite communication (VSATs), cellular base stations, WiMAX base stations, and other high-speed wireless communications infrastructure.
Details of the new technology were presented at the 2007 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS).
As wireless communication data-rates continue to become increasingly faster, power consumption in base stations - such as those for mobile phones – is also increasing. GaN HEMTs are promising as devices to realize lower power consumption for high power amplifiers in next-generation high-speed wireless communication systems. However, in order for GaN HEMTs to be used as high power, high voltage-endurance devices, they must maintain high reliability - a long lifespan – as it anticipated that they must withstand harsh usage conditions, including high temperatures and high drain voltages.
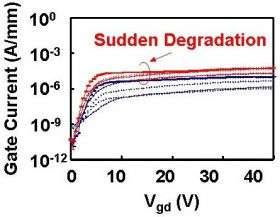
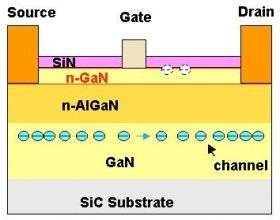
In long-term reliability testing, Fujitsu analyzed and discovered that in GaN HEMTs a correlation exists between gate leakage current and reliability. Furthermore, Fujitsu observed that the increase in gate leakage current depends on the quality of crystal and the structure of GaN HEMTs. Fujitsu improved crystal quality and optimized the layer structure to mitigate the electric field in a gallium-nitride HEMT structure with few surface traps by using its proprietary n-type GaN cap layer (surface layer).
Results of high-temperature pinch-off testing of these devices, operating at temperatures above 300°C confirmed long-term high reliability in excess of one million hours at channel temperatures of 200°C. This corresponds to a lifespan of more than 100 years, the most reliable in the world.
Pinch-off testing is the most severe reliability test, with high channel resistance and strong electric fields at the drain side of the transistor gate electrode . This is the world's first result in which such a long-term lifespan was confirmed under pinch-off condition with such a harsh testing factor as 50 V drain, as the previous record was at 28V maximum.
Source: Fujitsu