'Snow flea antifreeze protein' could help improve organ preservation
Scientists in Illinois and Pennsylvania are reporting development of a way to make the antifreeze protein that enables billions of Canadian snow fleas to survive frigid winter temperatures.
Their laboratory-produced first-of-a-kind proteins could have practical uses in extending the storage life of donor organs and tissues for human transplantation, the researchers indicate in a report scheduled for the July 9 issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
In the study, Stephen B. H. Kent and colleagues point out that scientists have tried for years to decipher the molecular structure and produce from chemicals in a laboratory the so-called "snow flea antifreeze protein (sfAFP)." Those steps are critical for obtaining larger amounts of the protein, which exists naturally in only minute quantities in snow fleas. The larger synthetic quantities can be used for further research and potential medical and commercial uses, they say.
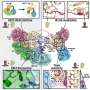
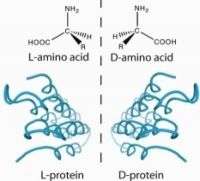
The researchers made synthetic sfAFP, and showed that it has the same activity as the natural protein. They also produced variants, including one form of sfAFP with a molecular architecture that is the reverse, or "mirror image," of natural sfAFP and different from any other protein found in living things on Earth. The mirror-image form of sfAFP appears less likely to trigger harmful antibodies and more resistant to destruction by natural enzymes, making it potentially more effective than the native form for use in organ and tissue preservation, the scientists note.
"Our most significant advance was the use of the two mirror image forms of the protein to determine the previously unknown crystal structure of this unique protein," said Kent. "That is a first in the history of protein X-ray crystallography."
Source: ACS