Metal sheets with DNA framework may enable nanocircuits
(PhysOrg.com) -- Using DNA not as a genetic material but as a structural support, Cornell researchers have created thin sheets of gold nanoparticles held together by strands of DNA. The work could prove useful for making thin transistors or other electronic devices.
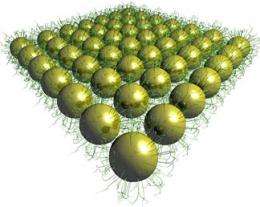
The research describing the creation of suspended, free-standing sheets of gold nanoparticles only 20 nanometers thick and held together by tangled, hairlike strands of DNA, is detailed in the May 4 Advance Online Publication of Nature Materials.
The work was led by Dan Luo, associate professor of biological engineering, and the team included first author and postdoctoral associate Wenlong Cheng;Christopher Umbach, assistant professor of materials sciences and engineering; and David Muller, associate professor of applied and engineering physics.
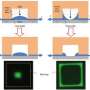
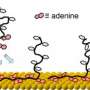
To make the thin, ordered sheets, called superlattices, the researchers attached gold nanoparticles to single-stranded DNA and submerged them in a water-based solution. They then deposited droplets of the solution onto a holey silicon substrate and allowed the water to evaporate.
What was left were thin sheets of gold nanoparticles, suspended in place by the DNA strands. What's more, Luo explained, the researchers demonstrated easy control of the sheets' mechanical properties by changing the lengths of the DNA or the distance between nanoparticles.
"We hope this can contribute to development of future nanocircuits," Luo said.
Provided by Cornell University (news : web)