Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter's first moon images available

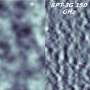
(PhysOrg.com) -- NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter has transmitted its first images since reaching the moon on June 23. The spacecraft's two cameras, collectively known as the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera, or LROC, were activated June 30. The cameras are working well and have returned images of a region in the lunar highlands south of Mare Nubium (Sea of Clouds).
As the moon rotates beneath LRO, LROC gradually will build up photographic maps of the lunar surface.

"Our first images were taken along the moon's terminator -- the dividing line between day and night -- making us initially unsure of how they would turn out," said LROC Principal Investigator Mark Robinson of Arizona State University in Tempe. "Because of the deep shadowing, subtle topography is exaggerated, suggesting a craggy and inhospitable surface. In reality, the area is similar to the region where the Apollo 16 astronauts safely explored in 1972. While these are magnificent in their own right, the main message is that LROC is nearly ready to begin its mission."
These images show cratered regions near the moon's Mare Nubium region, as photographed by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter's LROC instrument. Each image shows a region 1,400 meters (0.87 miles) wide. the bottoms of both images face lunar north. The image below shows the location of these two images in relation to each other.
LRO will help NASA identify safe landing sites for future explorers, locate potential resources, describe the moon's radiation environment and demonstrate new technologies.
The satellite also has started to activate its six other instruments. The Lunar Exploration Neutron Detector will look for regions with enriched hydrogen that potentially could have water ice deposits. The Cosmic Ray Telescope for the Effects of Radiation is designed to measure the moon's radiation environment. Both were activated on June 19 and are functioning normally.
Instruments expected to be activated during the next week and calibrated are the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter, designed to build 3-D topographic maps of the moon's landscape; the Diviner Lunar Radiometer Experiment, which will make temperature maps of the lunar surface; and the Miniature Radio Frequency, or Mini-RF, an experimental radar and radio transmitter that will search for subsurface ice and create detailed images of permanently-shaded craters.

The final instrument, the Lyman Alpha Mapping Project, will be activated after the other instruments have completed their calibrations, allowing more time for residual contaminants from the manufacture and launch of LRO to escape into the vacuum of space. This instrument is an ultraviolet-light imager that will use starlight to search for surface ice. It will take pictures of the permanently-shaded areas in deep craters at the lunar poles.
"Accomplishing these significant milestones moves us closer to our goals of preparing for safe human return to the moon, mapping the moon in unprecedented detail, and searching for resources," said LRO Project Scientist Richard Vondrak of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
While its instruments are being activated and tested, the spacecraft is in a special elliptical commissioning orbit around the moon. The orbit takes less fuel to maintain than the mission's primary orbit. The commissioning orbit's closest point to the lunar surface is about 19 miles over the moon's south pole, and its farthest point is approximately 124 miles over the lunar north pole.
After the spacecraft and instruments have completed their initial calibrations, the spacecraft will be directed into its primary mission orbit in August, a nearly-circular orbit about 31 miles above the lunar surface.
Goddard built and manages LRO, a NASA mission with international participation from the Institute for Space Research in Moscow. Russia provides the neutron detector aboard the spacecraft.
For more information about LRO's cameras and to view the first images, visit: lroc.sese.asu.edu
For more information about the LRO mission, visit: www.nasa.gov/lro
Source: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center (news : web)