New study resolves the mysterious origin of Merkel cells

A new study resolves a 130-year-old mystery over the developmental origin of specialized skin cells involved in touch sensation. The findings will appear in the October 5, 2009 issue of the Journal of Cell Biology.
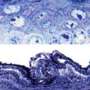
First described in 1875, Merkel cells are neuroendocrine cells that reside in the vertebrate epidermis, passing mechanical stimuli on to sensory neurons. In mice, they are mainly found in the paws and around the whiskers but, because they express proteins characteristic of both epithelial and neuronal cells, scientists have long debated whether Merkel cells develop from the epidermis or neural crest.
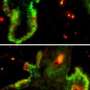
Van Keymeulen et al. traced the lineage of Merkel cells by fluorescently labeling cells derived from either epidermal or neural crest progenitors. This revealed that Merkel cells originally emerge from the embryonic epidermis. In addition, epidermal stem cells in adult mouse skin replenish the Merkel cell population as they slowly die off over time. The researchers also found that a transcription factor called Atoh1 is required for epidermal progenitors to differentiate into Merkel cells--mice lacking Atoh1 in their skin failed to develop any of the mechanotransducing cells.
Atoh1 acts as a tumor suppressor to prevent an aggressive skin cancer called Merkel cell carcinoma, says senior author Cédric Blanpain. His team now wants to investigate the precise function of the transcription factor in Merkel cell differentiation, as well as the signaling pathways that regulate the process.
More information: Van Keymeulen, A., et al. 2009. J. Cell Biol. doi:10.1083/jcb.200907080
Source: Rockefeller University (news : web)