DC-SCRIPT found to have prognostic value in breast cancer
DC-SCRIPT, or dendritic cell-specific transcript, is a key regulator of nuclear receptor activity that may have prognostic value in breast cancer, according to a new study published online December 14 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
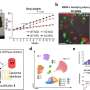
In this study, a team led by Gosse J. Adema, Ph.D., of the Department of Tumor Immunology, at the Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre, the Netherlands, and colleagues assessed the role of DC-SCRIPT as a co-regulator of nuclear receptors, including estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR)-B, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, and retinoic acid receptor alpha. Prognostic value was assessed in three independent cohorts of breast cancer patients.
The researchers found that DC-SCRIPT suppressed ER- and PR-mediated transcription in a ligand-dependent fashion, whereas it enhanced the activity of the other two receptors. Quantification of DC-SCRIPT mRNA expression in the three cohorts of patients revealed that this expression is an independent prognostic factor for breast cancer patients with ER- and/or PR-positive tumors, according to the authors.
In addition, they showed that breast tumors express lower levels of DC-SCRIPT mRNA than normal breast tissue and that breast tumor cell lines do not express it.
"On the basis of these findings, we hypothesize that the antiproliferative effect of DC-SCRIPT in breast cancer cells is mediated by modulating the activity of multiple nuclear receptors," the authors write. "It will be interesting therefore to also examine DC-SCRIPT expression levels in clinical trials that have explored the effect of stimulation of the RAR/RXR and PPAR/RXR pathways on the clinical outcome in breast cancer patients."
Source: Journal of the National Cancer Institute (news : web)