How are sadness and happiness like diseases? They're infectious, study finds
Is sadness a sickness? It appears to spread like one, a new study has found.
Researchers at Harvard University and MIT wanted to see if a mathematical model developed to track and predict the spread of infectious diseases such as SARS and foot-and-mouth disease could also apply to the spread of happiness -- and found that it worked.
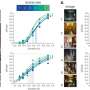
They used data collected from 1,880 subjects in the Framingham Heart Study, a long-term research effort that has followed subjects since 1948 (and added some new ones along the way), giving them physical and emotional exams every two years. At each visit, subjects were classified as content, discontent or neutral. The researchers monitored how these emotional states changed over time and how these changes depended on the emotions of the people with whom the participants came into contact.
When the information was put into a traditional infectious-disease simulation, slightly modified to reflect the unique qualities of emotional spread rather than actual disease, the researchers found a correlation between an individual's emotional state and those of the person's contacts.
In other words, it appears that you can catch happiness. Or sadness. Moreover, the "recovery time" doesn't depend on your contacts at all, which is a hallmark of diseases but surprising in an emotional context, since continuing contact with happy or sad people could be expected to affect one's emotional state even after the initial "infection."
People were found to "recover" (return to neutral) more quickly from discontent than from content; on average, a contentedness "infection" sticks around for 10 years, but it takes only five years to recover from discontent. While this may still seem like a long time, the work focused on long-term emotional states because they are more accurate measures of general life satisfaction than fleeting moods, which are already known to be contagious (think laughter).
On the other hand, sadness is more contagious than happiness: A single discontent contact doubles one's chances of becoming unhappy, while a happy contact increases the probability of becoming content by only 11 percent.
Researchers also found one way that emotions act differently than diseases -- they can arise due to events in your own life, such as a promotion or a disease diagnosis, rather than solely being "contagious." In another win for the good guys, it appears that happiness is more likely to come about spontaneously than is sadness.
A report of the emotions-as-diseases research has been published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
(c) 2010, Los Angeles Times.
Distributed by McClatchy-Tribune Information Services.