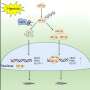
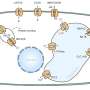
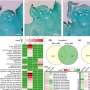
Protecting rice plants from heat when it attacks at nighttime
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is the staple food for more than half of the world's population. Based on mathematical modeling, worldwide cereal production is estimated to have a loss of 6%–7% yield per 1°C increase in seasonal ...