Study suggests that cells possess a hidden communication system
Cells constantly navigate a dynamic environment, facing ever-changing conditions and challenges. But how do cells swiftly adapt to these environmental fluctuations?

Cells constantly navigate a dynamic environment, facing ever-changing conditions and challenges. But how do cells swiftly adapt to these environmental fluctuations?
Cell & Microbiology
12 hours ago
0
102

Living beings can evolve to lose biological structures due to potential survival benefits from such losses. For example, certain groups of ray-finned fishes show such regressive evolution—medakas, minnows, puffera, and ...
Plants & Animals
Apr 23, 2024
0
0

With the naked eye, you can't see the weather in space, or feel the cosmic rays beaming down to Earth—but they can impact critical systems like our climate, computer connectivity, communications and even our health.
Astronomy
Apr 22, 2024
0
7
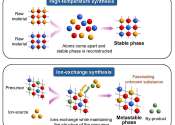
Tohoku University researchers have unveiled a new means of predicting how to synthesize new materials via the ion-exchange. Based on computer simulations, the method significantly reduces the time and energy required to explore ...
Analytical Chemistry
Apr 19, 2024
0
379

Until now, the generation and storage of electricity from solar energy has been dependent on various devices, leading to conversion losses. That may change soon, as chemists at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg ...
Analytical Chemistry
Apr 19, 2024
0
8

While it may not look like it, the interstellar space between stars is far from empty. Atoms, ions, molecules, and more reside in this ethereal environment known as the Interstellar Medium (ISM). The ISM has fascinated scientists ...
Analytical Chemistry
Apr 17, 2024
0
56

Researchers at ICIQ in Tarragona have developed a simple technique to produce microscopic crystals that activate in the presence of light, releasing silver ions with antimicrobial activity.
Bio & Medicine
Apr 17, 2024
0
58
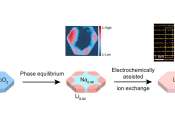
Ion exchange is a powerful technique for converting one material to another when synthesizing new products. In this process, scientists know what reactants lead to what products, but how the process works—the exact pathway ...
Analytical Chemistry
Apr 16, 2024
0
10

Chemists at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory have invented a more efficient way to extract lithium from waste liquids leached from mining sites, oil fields, and used batteries. They demonstrated that ...
Analytical Chemistry
Apr 16, 2024
1
38
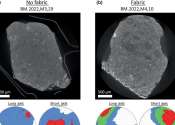
Intensive new nano-analysis of the Winchcombe meteorite has revealed how it was affected by water and repeatedly smashed apart and reassembled on the journey it took through space before landing in an English sheep field ...
Planetary Sciences
Apr 15, 2024
0
85
An ion is an atom or molecule where the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge.
Since protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged, if there are more electrons than protons, the atom or molecule will be negatively charged. This is called an anion (pronounced /ˈænaɪən/; an-eye-on), from the Greek ἀνά (ana), meaning 'up'.
Conversely, if there are more protons than electrons, the atom or molecule will be positively charged. This is called a cation (pronounced /ˈkætaɪən/; cat-eye-on), from the Greek κατά (kata), meaning 'down'.
An ion consisting of a single atom is called a monatomic ion. If it consists of two or more atoms, it is called a polyatomic ion. Polyatomic ions containing oxygen, such as carbonate and sulfate, are called oxyanions.
When writing the chemical formula for an ion, its charge is written as a superscript '+' or '−' following a number indicating the difference between the number of protons and the number of electrons. The number is omitted if it is equal to 1. For example, the sodium cation is written as Na+, the '+' indicating that it has one less electron than it has protons. The sulfate anion is written as SO42−, the '2−' indicating that it has two more electrons than it has protons.
If an ion contains unpaired electrons, it is called a radical ion. Just like neutral radicals, radical ions are very reactive.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA