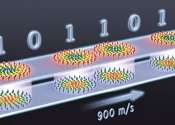
Enhancing memory technology: Multiferroic nanodots for low-power magnetic storage
Traditional memory devices are volatile and the current non-volatile ones rely on either ferromagnetic or ferroelectric materials for data storage. In ferromagnetic devices, data is written or stored by aligning magnetic ...