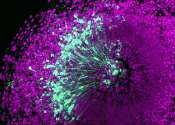
Organoids research identifies factor involved in brain expansion in humans
What makes us human? According to neurobiologists it is our neocortex. This outer layer of the brain is rich in neurons and lets us do abstract thinking, create art, and speak complex languages. An international team led ...