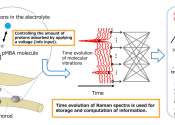
High-precision blood glucose level prediction achieved by few-molecule reservoir computing
A collaborative research team from NIMS and Tokyo University of Science has successfully developed an artificial intelligence (AI) device that executes brain-like information processing through few-molecule reservoir computing. ...