Machine learning classifies 191 of the world's most damaging viruses
Researchers from the University of Waterloo have successfully classified 191 previously unidentified astroviruses using a new machine learning-enabled classification process.
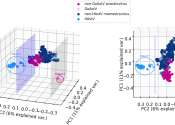
Researchers from the University of Waterloo have successfully classified 191 previously unidentified astroviruses using a new machine learning-enabled classification process.
Molecular & Computational biology
2 hours ago
0
0

NASA is working to resume science operations of the agency's Hubble Space Telescope after it entered safe mode April 23 due to an ongoing gyroscope (gyro) issue. Hubble's instruments are stable, and the telescope is in good ...
Astronomy
3 hours ago
0
8

More than 100 years ago, astronomer George Ellery Hale brought two Pasadena institutions together to build what was then the largest optical telescope in the world. The Mount Wilson Observatory changed the conception of humankind's ...
Astronomy
5 hours ago
0
34

A new type of porous material that can store carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases has been developed by a team of scientists jointly led by Heriot-Watt University in Edinburgh, Scotland.
Analytical Chemistry
7 hours ago
0
41
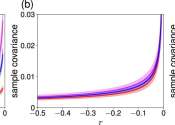
Whether you're trying to predict a climate catastrophe or mental health crisis, mathematics tells us to look for fluctuations.
Mathematics
Apr 26, 2024
1
219
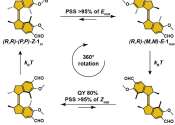
Light-driven molecular motors were first developed nearly 25 years ago at the University of Groningen, the Netherlands. This resulted in a shared Nobel Prize for Chemistry for Professor Ben Feringa in 2016. However, making ...
Biochemistry
Apr 26, 2024
0
127

Several years ago, a team of scientists from MIT and the University of Massachusetts at Lowell designed and deployed a first-of-its-kind web programming course for incarcerated individuals across multiple correctional facilities. ...
Social Sciences
Apr 25, 2024
0
13

ESA's Hera asteroid mission for planetary defense will make a swingby of Mars next March, borrowing speed to help reach its target Didymos binary asteroid system.
Planetary Sciences
Apr 25, 2024
0
35

PFAS, or forever chemicals, are widespread and more likely to be found in public water systems serving low-income communities and communities of color in New Jersey, according to new research from Northeastern University.
Environment
Apr 25, 2024
0
7

China launched a three-member crew to its orbiting space station on Thursday as part of its ambitious program that aims to put astronauts on the moon by 2030.
Space Exploration
Apr 25, 2024
0
13
Science (from the Latin scientia, meaning "knowledge") refers to any systematic knowledge-base or prescriptive practice that is capable of resulting in a prediction or predictable type of outcome. In this sense, science may refer to a highly skilled technique or practice.
In its more restricted contemporary sense, science refers to a system of acquiring knowledge based on scientific method, and to the organized body of knowledge gained through such research. This article focuses on the more restricted use of the word. Science as discussed in this article is sometimes called experimental science to differentiate it from applied science—the application of scientific research to specific human needs—although the two are often interconnected.
Science is a continuing effort to discover and increase human knowledge and understanding through disciplined research. Using controlled methods, scientists collect observable evidence of natural or social phenomena, record measurable data relating to the observations, and analyze this information to construct theoretical explanations of how things work. The methods of scientific research include the generation of hypotheses about how phenomena work, and experimentation that tests these hypotheses under controlled conditions. Scientists are also expected to publish their information so other scientists can do similar experiments to double-check their conclusions. The results of this process enable better understanding of past events, and better ability to predict future events of the same kind as those that have been tested.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA