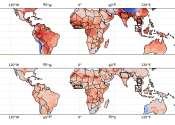
Record-breaking heat and humidity predicted for tropics this summer
A new statistical analysis of the interaction between El Niño and rising global temperatures due to climate change concludes that the approaching summer in the tropics has nearly a 7 in 10 chance of breaking records for ...